EU Regulation 2017/313 brought clarity and specified 21st century requirements to technology as well as precisely described the requirements for service providers in terms of ATSEP training and competence assessment. This article examines the wider context and summarises the implications for ATSEP qualification.
Rules and regulations are the foundation of the European Union civil aviation system.
EASA's ED Decision 2020/020/R and the Easy Access Rules to facilitate the Regulation's uniform implementation. The rules break down and operationalize the learning objectives to a curriculum level, detailing objectives and summarizing content.
Higher density and technical complexity call for a 21sth century pan-European ATC
Air traffic is becoming denser and technology more complex - spreading across various air spaces to be reactive, dynamic and foresightful. Maintaining and servicing these connected systems requires reliable technology and highly skilled ATSEP.
For years, ATCO qualification has been well regulated. Consequently, the training programs were well defined and supported by powerful simulators, training programs as well as training-time on and off the workplace to maintain and develop the competences.
In contrast to this ATSEP qualification appeared to exist in the background. Training objectives were last updated 2008. They neither covered new technological developments such as remote-towers, data centre approaches of air traffic services (ATS), latest network technologies, nor did it include the Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) deployment (EASA Explanatory Note to Decision 2020/020/R).
EU Regulation 2017/313
EU Regulation 2017/313 brought clarity and specified 21st century requirements to technology as well as precisely described the requirements for service providers in terms of training and competence assessment.
The advantage of an EU Regulation in contrast to an EU Directive is that it is set into force centrally by the EU Commission without the requirement of needing to be ratified by the national governments. This makes regulations faster to implement, without any national modifications or interpretations.
EASA and the national supervisory authority and service providers
ATSEP training and competence assessment are regulated in Annex XIII of the regulation. The "minimum requirements to be met with respect to the training and the competence assessment of ATSEP may be determined by the competent authority." These are in most cases the national supervisory authority. The exception are data service providers and network managers, which are considered pan-European services, and therefore managed by EASA.
EASA is in the position of the central coordinator, maintaining a database of contact details of the competent authorities. The competent authorities are equipped with strong stakeholding power of audit and monitoring, having access to the service provider's premises and documents at any moments, in compliance with applicable national law.
Paragraph ATSEP.OR.105 of the EU Regulation regulates training and assessment, specifying that "the service provider employing ATSEP shall establish a training and competence assessment programme to cover the duties and responsibilities to be performed by ATSEP."
Given the distributed responsibility for supervision and implementation of the defined objectives, varying approaches to the implementation and audit of the syllabus and training material can be expected.
EASA Decision 2017/001/R and Amendment ED Decision 2020/020/R
In 2017, EASA together with the involved stakeholders published Decision 2017/001/1, specifying Acceptable Means of Compliance and Guidance Material to the Part-PERS (Annex XIII of the EU Regulation). Part-PERS is the section of the Regulation covering training and assessment. Through this Decision, EASA and it's collaborators aim to facilitate the uniform implementation of the implementing rules (IR) requirements covered by Regulation (EU) 2017/373.
In 2020, EASA provided the ED Decision 2020/020/R as an amendment to its predecessor, updating training objectives, course structure as well as introducing new courses that better reflect technical evolution or take into account lessons learnt during the first 3 years of operation. In addition, the 2020 version corrected typographical and editorial errors (explanatory Note to ED Decision 2020/020/R).
It is important to note that neither the Acceptable Means of Compliance (AMC) nor the Guidance Material (GM) are binding. The sole document providing Implementing Rules (IR) which is binding in its entirety is the EU Regulation. As EASA puts it, the "AMC serves as a means by which the requirements contained in the Basic Regulation, and the IR, can be met. However, applicants may decide to show compliance with the requirements using other means ..." Also the Guidance Material is "non-binding explanatory and interpretation material on how to achieve the requirements" (FAQ-n.19026).
EASA's Easy Access Rules for ATM-ANS (Regulation (EU) 2017/373)
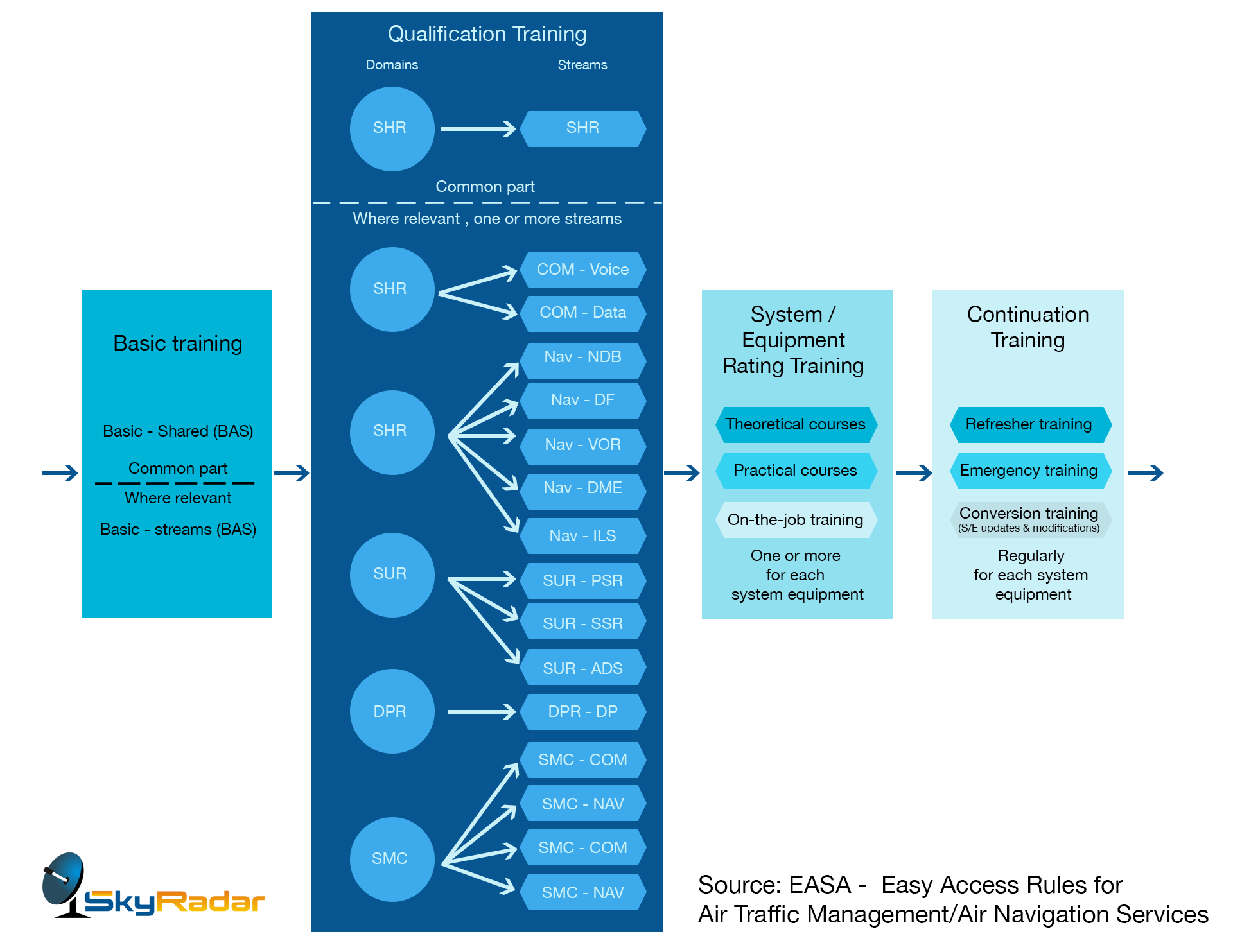
The above defined documents are of course written using terminology that at times, is not easy to interpret. They are high level and can be challenging to implement or put into practice. As a result, EASA released the illustrated Easy Access Rules for ATM-ANS, which are color coded, detailed and illustrated. The section ANNEX XIII - PART-PERS defines the "REQUIREMENTS FOR SERVICE PROVIDERS CONCERNING PERSONNEL TRAINING AND COMPETENCE ASSESSMENT".
Functionally, EASA categorizes the ATSEP competence fields (just like ICAO) into
- Communication
- Navigation
- Surveillance
- Data-processing / automation
- System monitoring and control
EASA Easy Access Rules and ICAO 10057
The above described Easy Access Rules dive deeper in the specification of learning objectives than the ICAO Doc 10057. The Rules cover all of Doc 10057 contents and foster their implementation of a high quality level.
SkyRadar's ATSEP training solutions for aviation academies
SkyRadar and its solution partners provide a modular and holistic training infrastructure for ATSEP qualification, enabling both ANSPs and aviation academies to comply with the easy access rules effectively, pedagogically optimized, and in a time- and cost-effective way.
It includes state-of-the-art sub-systems such as miniaturized pulse / Doppler radars, digital signal processing, voice communication systems, a real air traffic control system, Safetynets, system monitoring and control, or SOC/CSIRT oriented cybersecurity. It also includes modern technical features like virtualization and remote towers.
Talk to us to learn more about the suitable training infrastructure to implement your EU 2017/373 oriented laboratories.
Stay tuned! to receive more updates on SkyRadar's training solutions for ATSEP.