The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) have developed requirements for the structuring of ATSEP training. While ICAO’s requirements in its training structure apply worldwide, EASA’s requirements for training apply to ATSEP in European countries and slightly differ from ICAO’s requirements.
Structure of ICAO’s ATSEP Competency-Based Training
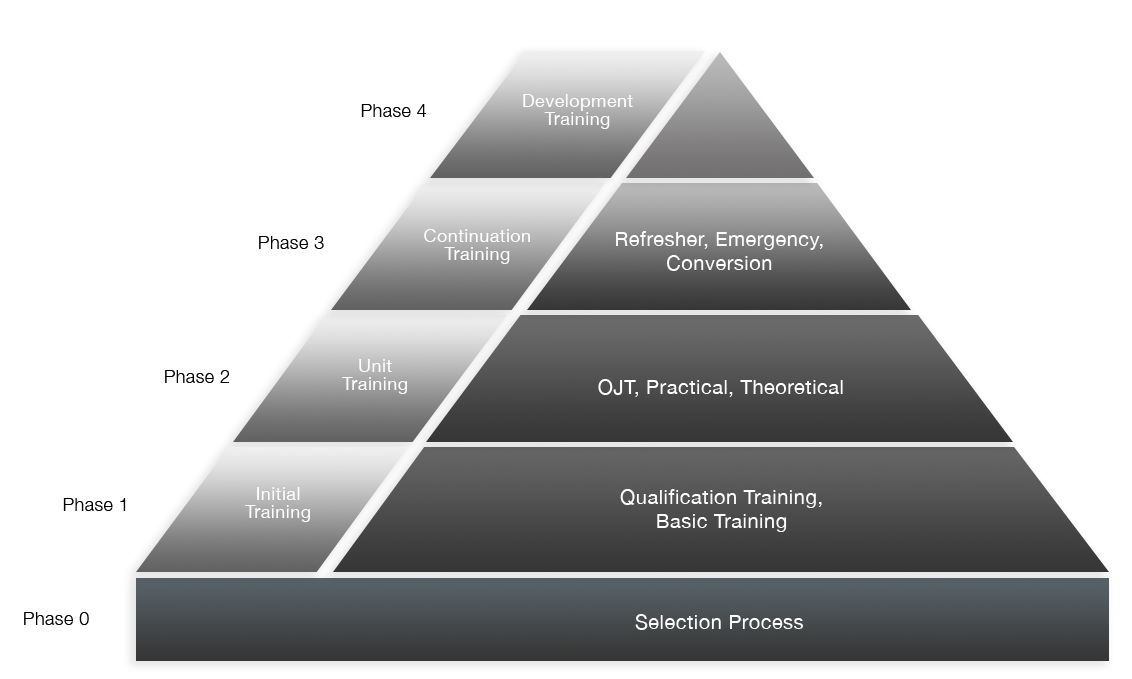
The ICAO recommends that ATSEP training programs be organized into phases
0 through 4:
- Phase 0 is the ATSEP Selection Process. This is where the air navigation service provider (ANSP) selects candidates according to its ATSEP profiles and activities.
- Phase 1 is the Initial Training Phase. It is designed to give the ATSEP candidate the needed basic knowledge and skills. This is delivered in two parts:
1. Basic training that applies to all ATSEP
2. Qualification training that is specific to applicable ATSEP profiles
- Phase 2 is Unit Training. This phase begins after the successful completion of Phase 1. The training consists of activities that will be performed by the ATSEP in a specific environment. Unit training contains theoretical and practical issues related to equipment-specific and/or site-specific perspectives. It also includes on-the-job training. ATSEP competencies are trained and assessed during this phase.
- Phase 3 is Continuation Training. It is designed to help ATSEP maintain their competencies and prepare for system upgrades and/or modifications. This includes conversion, refresher and emergency training.
- Phase 4 is Development Training. The training in this phase focuses on developing additional competencies that are required because of a change or evolution in an ATSEP’s profile, including moving to a higher position.
Understanding ATSEP Training Paths
An ATSEP will need to go through training during different points throughout his career. However, the usual path is that the ATSEP will begin at the selection phase and continue until the unit training phase is completed. After that, ATSEP will participate in continuation training phase to maintain their competencies. An ATSEP will be required to go back for training at different phases if:
- There is a change on the system that the ATSEP already works with. This would fall under continuation training.
- The ATSEP switches from one domain to another like changing navigation to surveillance. He would either go back for initial training or unit training.
- The ATSEP is changing his activities that requires the need for additional competencies like moving up to system implementation from maintenance operations. This would require development training.
- An additional system will be operated by the ATSEP. This would require additional unit training.
ICAO’s Certificates of Competence the ATSEP
After completing the appropriate training, the forms of certificates of competence may include:
- A license from the authority
- A certificate from an ANSP or the training organization
- An academic degree or diploma from an accredited educational institution
Structure of EASA’s ATSEP Competency-Based Training
EASA’s document Acceptable Means of Compliance (AMC) and Guidance Material (GM) to Part-PERS – Requirements for Service Providers Concerning Personnel Training and Competence Assessment explains the training structure that pertain to ATSEP working in the European Union. The requirements are like that of which is required of ATSEP trained according to the ICAO training requirements but do differ in some ways.
ATSEP following EASA’s competency-based training will follow this path:
- Basic Training
- Qualification Training that requires the completion of a minimum of one qualification stream
- System/Equipment Training that requires at least one system/equipment rating in the ATSEP’s chosen stream
- Continuation Training as needed or required that consists of:
- Refresher
- System Equipment Modifications
- System/Equipment Upgrades
- Emergency
Basic training may be taken as a stand-alone or as part of a larger initial training course such as basic and qualification training. When ATSEP move to another service provider, the new provider may perform a competence assessment of the ATSEP’s previous training. When shortcomings are found that are related to the ATSEP’s new duties, these deficiencies should be addressed through additional training as needed. The ATSEP’s language proficiency is also taken into consideration to ensure if needed, the ATSEP can communication across operational boundaries where a common language is required.
Learn more about ATSEP training equipment.





