STC Alarm receiver errors affect Air Traffic Control (ATC) safety and efficiency. This article defines, illustrates, and offers solutions to prevent these errors.
Definition of Receiver Errors Due to STC Alarm
Receiver errors due to STC Alarm refer to errors in the reception of signals from an aircraft's transponder by the ATC system. These errors can occur due to various reasons, such as hardware failures, software malfunctions, or communication issues. STC Alarm is a specific type of receiver error that occurs when the ATC system does not receive any signal from an aircraft's transponder for a certain period. The duration of this period depends on the configuration of the ATC system and the specific requirements of the airspace in which the aircraft is flying.
What is STC Alarm?
STC Alarm is a specific type of receiver error that occurs when there is a loss of communication between the ATC and the aircraft's transponder. STC stands for "Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) Transponder Code," which is a unique code assigned to an aircraft's transponder by the ATC system. The transponder continuously transmits this code to the ATC system, which uses it to identify the aircraft and track its movement. In case of STC Alarm, the ATC system does not receive any signal from the transponder for a specific period, which triggers an alarm in the ATC system.An ATSEP is responsible for the maintenance and repair of the ATC system. In case of STC Alarm, the ATSEP would receive an alarm notification from the ATC system and would have to investigate the cause of the alarm. The ATSEP would first check the hardware and software components of the ATC system to ensure that they are functioning correctly. If no issues are found in the ATC system, the ATSEP would then contact the pilot of the aircraft to troubleshoot the transponder. If the problem is not resolved, the ATSEP may have to request the pilot to change the transponder or perform further maintenance.
Scenario Illustrating the Impact of receiver Error Related to STC Alarm on ATC Services
Scenario 1: Receiver Error Causing STC Alarm Failure
Imagine an air traffic control center responsible for managing the flow of aircraft in and out of a major international airport. The center is equipped with sophisticated Surveillance and Tracking Control (STC) alarms that provide critical information about aircraft positions, altitudes, and velocities. However, due to a receiver error, the STC alarms fail to function properly.
Impact on Air Traffic Control Services
Loss of Situational Awareness
The failure of the STC alarms due to receiver errors can significantly impact the situational awareness of air traffic controllers. Without accurate and timely information about aircraft positions and movements, controllers may struggle to maintain a clear picture of the airspace, increasing the risk of conflicts, near misses, and potential accidents.
Delayed Response and Increased Workload
In the absence of functioning STC alarms, controllers may need to rely on alternative sources of information, such as radar screens and verbal communications, to track and monitor aircraft. This can result in delayed response times and an increased workload for the controllers, as they need to manually process and interpret data from various sources, increasing the risk of errors and congestion in the airspace.
Scenario 2: Receiver Error Causing False Alarms and Unreliable Information
In another scenario consider an air traffic control center that uses receiver systems to collect and process data from aircraft transponders. However, due to a receiver error, false alarms and unreliable information start to occur.
Impact on Air Traffic Control Services
Confusion and Distraction
The occurrence of false alarms and unreliable information due to receiver errors can create confusion and distractions for air traffic controllers. They may be inundated with a high volume of false alerts, which can lead to reduced trust in the alarm system and increased difficulties in distinguishing genuine alerts from false ones, affecting their decision-making process.
Safety Risks and Operational Challenges
False alarms and unreliable information can introduce safety risks and operational challenges in air traffic control services. Controllers may find it challenging to accurately track aircraft, determine their positions, and issue appropriate instructions. This can lead to inefficiencies, delays in flight operations, and potentially hazardous situations if critical instructions are not correctly communicated or if false alerts divert attention from genuine safety concerns.
In both scenarios, receiver errors related to STC alarms can have significant implications for air traffic control services. They can compromise situational awareness, increase workload, delay response times, and introduce safety risks. It emphasizes the critical importance of maintaining reliable and properly functioning receiver systems in air traffic control to ensure the safe and efficient management of aircraft.
Impact of receiver Errors Related to STC Alarm on ATC Services
Receiver errors related to the STC (Standard Terminal Automation Replacement System) alarm can have a significant impact on air traffic control services. The STC is a critical system used by ATC (Air Traffic Control) to manage the flow of air traffic in terminal areas. If there is a receiver error related to the STC alarm, it can lead to serious safety concerns and disruptions in air traffic.
One of the main impacts of receiver errors related to the STC alarm is the inability of ATC to accurately track the position of airplanes. This can lead to a breakdown in communication between the ATC and the pilot, and result in delayed or missed instructions. If the ATC cannot accurately track an airplane's position, they cannot provide the necessary guidance to avoid potential conflicts or hazards such as other aircraft or weather conditions.
Additionally, receiver errors related to the STC alarm can lead to communication breakdowns between the ATC and the pilot. This can result in miscommunications or missed instructions, which can create confusion and delay in the flow of air traffic. It can also increase the risk of accidents or incidents if the pilot is not aware of critical information such as altitude or heading changes.
Another impact of receiver errors related to the STC alarm is a reduction in the overall efficiency of air traffic control services. If there are delays or disruptions in the flow of air traffic, it can result in longer flight times, missed connections, and increased fuel consumption, which can have a negative impact on the environment.
In summary receiver errors related to the STC alarm can have a significant impact on air traffic control services. It can lead to safety concerns, communication breakdowns, delays, and a reduction in the overall efficiency of air traffic control services. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure regular maintenance and testing of equipment to prevent receiver errors related to the STC alarm.
Steps to be Taken by ATSEP in Rectification of Receiver Errors Related to STC Alarm
In case of receiver errors related to STC Alarm, ATSEP should take the following steps for rectification
Identify the Error
ATSEP should first identify the specific error or alarm message associated with the receiver system. This can be done by reviewing system logs, error codes, or alarm indications displayed on the equipment.
Perform Initial Checks
ATSEP should conduct initial checks to ensure that the error is not caused by simple issues such as loose connections, power supply problems, or environmental factors. They should inspect cables, connectors, and power sources to ensure they are properly connected and functioning.
Consult Technical Documentation
ATSEP should refer to the technical documentation provided by the equipment manufacturer or system vendor. This documentation will contain troubleshooting guides, error code explanations, and recommended rectification procedures specific to the receiver system.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
ATSEP should follow the guidelines provided by the manufacturer for troubleshooting and rectification. This may involve step-by-step instructions for identifying and resolving common receiver errors related to STC alarm. The guidelines may also include safety precautions and specific procedures to be followed.
Check Configuration and Settings
ATSEP should review the configuration and settings of the receiver system. They should ensure that the system is configured correctly according to the required parameters and specifications. Any incorrect settings should be corrected as per the manufacturer's recommendations.
Perform Diagnostic Tests
ATSEP should utilize diagnostic tools or built-in diagnostic capabilities of the receiver system to perform tests. These tests may include signal quality checks, receiver performance evaluations, or system self-tests. The results of these tests can help in identifying the root cause of the error.
Analyze Error Logs
ATSEP should analyze the error logs and data collected from the receiver system to gain insights into the nature and frequency of the errors. This analysis can help in identifying patterns or recurring issues, which may require further investigation or specialized support from the manufacturer.
Collaborate with Technical Support
If the error persists or requires advanced troubleshooting, ATSEP should collaborate with technical support teams from the manufacturer or system vendor. They can provide specialized guidance, remote assistance, or on-site support to resolve complex receiver errors related to STC alarm.
Conduct Maintenance and Repairs
ATSEP should perform maintenance tasks and repairs as necessary. This may involve replacing faulty components, updating firmware or software, cleaning or calibrating the receiver system, or implementing hardware modifications as recommended by the manufacturer.
Test and Verify
After rectifying the receiver error, ATSEP should conduct thorough testing and verification of the system to ensure that the error has been successfully resolved. This may involve conducting functional tests, performance evaluations, or simulated operational scenarios to validate the proper functioning of the receiver system.
Document Rectification Actions
ATSEP should document all the rectification actions taken, including the steps performed, changes made, components replaced, and any other relevant information. This documentation serves as a reference for future troubleshooting, maintenance, or audits.
Continuous Monitoring and Preventive Measures
ATSEP should establish a system for continuous monitoring of the receiver system to detect and address any potential errors or anomalies promptly. Additionally, they should implement preventive maintenance procedures, regular inspections, and software updates as recommended by the manufacturer to minimize the occurrence of receiver errors related to STC alarm.
Steps to be Followed by ATSEP for Preventing STC Alarm
ATSEP can take the following steps to prevent STC Alarm
Regular System Inspections
ATSEP should conduct regular inspections of the receiver system to ensure its proper functioning. This includes checking for loose connections, damaged cables, and any physical issues that may impact the system's performance.
Antenna Maintenance
The antenna plays a crucial role in receiving signals accurately. ATSEP should perform routine maintenance on the antenna, including cleaning, checking for proper alignment, and inspecting for any damage. They should also ensure that there are no obstructions blocking the antenna's line of sight to the signal source.
Power Supply Monitoring
ATSEP should monitor the power supply of the receiver system to ensure it is stable and within the required voltage range. They should regularly check for any fluctuations or abnormalities that could affect the system's performance and take appropriate measures to address them.
Regular Firmware and Software Updates
Manufacturers often release firmware and software updates to improve system performance and address known issues. ATSEP should stay updated with the latest releases and perform regular updates on the receiver system. This helps ensure that the system is operating with the most stable and secure software version.
Signal Quality Monitoring
ATSEP should monitor the signal quality of the receiver system to detect any degradation or anomalies. This can be done using built-in diagnostic tools or specialized equipment. By monitoring the signal quality, ATSEP can identify potential issues before they lead to STC alarms and take necessary preventive actions.
Environmental Monitoring
The receiver system's performance can be affected by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference. ATSEP should monitor the environment around the system and take measures to maintain optimal conditions. This may include using proper ventilation, shielding against interference, and implementing temperature and humidity control measures.
Conduct Periodic Calibration
ATSEP should perform periodic calibration of the receiver system to ensure its accuracy and reliability. Calibration helps maintain the system's performance within specified tolerances and compensates for any drift or variation that may occur over time. Following the manufacturer's guidelines, ATSEP should schedule and perform calibration procedures accordingly.
Implement Redundancy and Backup Systems
To enhance system reliability and minimize the risk of STC alarms, ATSEP can implement redundancy and backup systems. This involves setting up duplicate components or systems that can automatically take over if the primary system fails. Redundancy helps ensure continuous operation and reduces the impact of failures or errors.
Maintain Documentation
ATSEP should maintain comprehensive documentation related to the receiver system, including configuration settings, maintenance records, calibration reports, and any changes made to the system. This documentation serves as a reference for troubleshooting, system audits, and future maintenance activities.
Continuous Training and Professional Development
ATSEP should engage in continuous training and professional development activities to stay updated with the latest advancements, best practices, and industry standards related to receiver systems. This enables them to proactively identify potential issues, implement preventive measures, and effectively respond to any emerging challenges.
Factors Responsible for STC Alarm Related Receiver Errors
Several factors can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors, such as
Communication Issues
Communication issues between the ATC and aircraft's transponder can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors.
Hardware Failures
Hardware failures in the ATC system or aircraft's transponder can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors.
Software Malfunctions
Software malfunctions in the ATC system or aircraft's transponder can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as electromagnetic interference can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors.
Human Error
Human error in the maintenance or operation of the ATC system or aircraft's transponder can cause STC Alarm related receiver errors.
Some Common Types of Receiver Errors Caused by STC Alarm
Some common types of receiver errors caused by STC Alarm are
False Targets
False targets can appear on the ATC system due to STC Alarm related receiver errors, leading to confusion and potential safety hazards.
Inaccurate Positioning
Inaccurate positioning of aircraft can occur due to STC Alarm related receiver errors, leading to potential conflicts and safety hazards.
Delayed Updates
Delayed updates of aircraft's position and other essential information can occur due to STC Alarm related receiver errors, leading to potential safety hazards.
Impact of STC Alarm Related Receiver Errors
The impact of STC Alarm related receiver errors can be significant on the safety and efficiency of ATC services. Some of the impacts are:
Safety Hazards
STC Alarm related receiver errors can cause potential safety hazards such as collisions, near-misses, and conflicts between aircraft.
Delays
STC Alarm related receiver errors can lead to delays in the ATC system, as the system may have to reroute other aircraft to avoid potential conflicts with the untracked aircraft.
Congestion
STC Alarm related receiver errors can cause congestion in the airspace, as the ATC system may have to reroute other aircraft to avoid potential conflicts with the untracked aircraft.
Loss of Data
STC Alarm related receiver errors can cause the loss of important data such as aircraft's position, altitude, and speed, leading to potential safety hazards.
Research Highlights
Causes and Identification
Studies aim to identify the root causes of receiver errors related to STC Alarm, such as equipment malfunction, electromagnetic interference, or software issues. This helps in developing effective prevention strategies.
Impact on ATC Services
Research examines the impact of receiver errors on the safety and efficiency of ATC services. It investigates potential safety hazards, delays, congestion, and loss of data caused by STC Alarm-related errors.
Prevention Strategies
Efforts are made to develop preventive measures and guidelines for Air Traffic Safety Electronics Personnel (ATSEP). This includes improving equipment reliability, implementing redundancy systems, and training ATSEP on detecting and rectifying receiver errors.
Incident Analysis
Researchers analyze aviation incidents and near-misses related to receiver errors due to STC Alarm. These analyses provide valuable insights into the consequences of such errors and help in improving ATC systems and procedures.
Communication Protocols
Research explores the development of robust communication protocols and protocols for reestablishing communication during STC Alarm situations. This involves studying communication failures, protocol implementation, and identifying areas for improvement.
Conclusion
STC Alarm related receiver errors can have significant impacts on the safety and efficiency of ATC services. It is essential for ATSEP to take proactive steps to prevent and rectify receiver errors related to STC Alarm. Regular maintenance, software updates, training, and redundancy can help to prevent errors due to STC Alarm. By implementing these measures, the ATC system can ensure the safety and efficiency of the airspace, which is crucial for the aviation industry.
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control Solution
SkySMC - SkyRadar’s System Monitoring and Control Suite is a pedagogically enhanced, fully operational monitoring & control tool. It has been designed to practice these use cases. We have optimized it to host ATSEP training in SUR, NAV, COM, DPR and SMC compliant to EASA's Easy Access Rules for ATM-ANS (Regulation (EU) 2017/373) and ICAO Doc 10057.
SkyRadar provides SkySMC as a complete laboratory in a turn-key approach, or as a virtual infrastructure (for purchase or as a service).
SkySMC is not a simulator, but a fully operational open monitoring system. It comes by default with a server including various virtualized applications and virtualized servers, but also connects to simulated systems. In addition, there are various hardware extensions available including training infrastructures, monitorable training radars, or even complete ATM systems, all connected to the System Monitoring & Control solution. Most components such as the radars, it IT infrastructure or networks exist in hardware and software (virtualized or simulated).
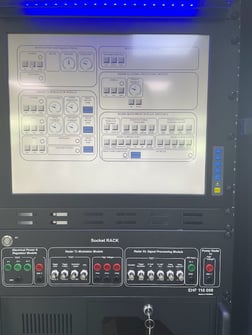
The two photos above show the same trouble-shooting panel and socket rack in real hardware and in the simulator (fully functioning).
SkyRadar's System Monitoring & Control training system can be easily blended into distance learning solutions and existing learning management systems.
Let's talk
Stay tuned to be always the first to learn about new use cases and training solutions in ATSEP qualification (real radars or simulators).
Or simply talk to us to discuss your training solution.
References
- Aviation Safety Network. (2016). Incident: Swiss A320 at Zurich on Dec 29th 2016, communication failure leads to airspace closure. https://aviation-safety.net/wikibase/191484
- Aviation Safety Network. (2018). Incident: Delta B763 near London on Jul 10th 2018, STC alarm causes loss of ADS-B data. https://aviation-safety.net/wikibase/213085
- Federal Aviation Administration. (2018). Advisory Circular 90-105A: Approval Guidance for Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) Out Systems. https://www.faa.gov/documentLibrary/media/Advisory_Circular/AC_90-105A_Chg_1.pdf